Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 La and evaluation of resonance parameters
La and evaluation of resonance parametersEndo, Shunsuke; Kawamura, Shiori*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Yoshikawa, Hiromoto*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki
European Physical Journal A, 59(12), p.288_1 - 288_12, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 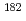 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
Tei, C.; Otaka, Masahiko; Kuwahara, Daisuke*
Chemical Physics Letters, 829, p.140755_1 - 140755_6, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)We were able to detect the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal of a liquid sodium clinging to the interface of solid metal particles for the first time. In this study, we confirmed the difference in the relaxation times due to the difference in the interactions between liquid sodium and metal particles suspended in the liquid sodium. It was found that the surface of the micro titanium particles and liquid metallic sodium interact physically, not chemically.
Hironaka, Kota; Lee, J.; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Ito, Fumiaki*; Hori, Junichi*; Terada, Kazushi*; Sano, Tadafumi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1054, p.168467_1 - 168467_5, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation) SR) methods
SR) methodsIto, Takashi; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Hydrogenomics; The Science of Fully Utilizing Hydrogen (Internet), p.43 - 49, 2023/03
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-063, 86 Pages, 2023/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "The study of oxidative stress status in the organs exposed to low dose/low dose-rate radiation" conducted from FY2019 to FY2021. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to investigate the biological effects of low dose/low dose-rate radiation exposure, which is of great social interest, on the oxidative stress status of individual organs and will contribute to the collection of scientific data in a dose range to be required. The samples to be analyzed in this study were collected from wild Japanese macaques exposed in the ex-evacuation zone after the accident of 1F.
 -wave
-wave 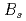 states combining quark model and lattice QCD in the coupled channel framework
states combining quark model and lattice QCD in the coupled channel frameworkYang, Z.*; Wang, G.-J.*; Wu, J.-J.*; Oka, Makoto; Zhu, S.-L.*
Journal of High Energy Physics (Internet), 2023(1), p.058_1 - 058_19, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.82(Physics, Particles & Fields)Combining the quark model, the quark-pair-creation mechanism and 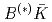 interaction, we have investigated the near-threshold
interaction, we have investigated the near-threshold  -wave
-wave 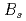 states in the framework of the Hamiltonian effective field theory. With the heavy quark flavor symmetry, all the parameters are determined in the
states in the framework of the Hamiltonian effective field theory. With the heavy quark flavor symmetry, all the parameters are determined in the 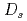 sector by fitting the lattice data. The masses of the bottom-strange partners of the
sector by fitting the lattice data. The masses of the bottom-strange partners of the 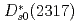 and
and 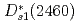 are predicted, which are well consistent with the lattice QCD simulation. The two
are predicted, which are well consistent with the lattice QCD simulation. The two  -wave
-wave 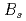 states are the mixtures of the bare
states are the mixtures of the bare 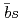 core and
core and 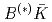 component. Moreover, we find a crossing point between the energy levels with and without the interaction Hamiltonian in the finite volume spectrum in the
component. Moreover, we find a crossing point between the energy levels with and without the interaction Hamiltonian in the finite volume spectrum in the 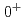 case, which corresponds to a CDD (Castillejo-Dalitz-Dyson) zero in the
case, which corresponds to a CDD (Castillejo-Dalitz-Dyson) zero in the  -matrix of the
-matrix of the 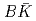 scattering. This CDD zero will help deepen the insights of the near-threshold states and can be examined by future lattice calculation.
scattering. This CDD zero will help deepen the insights of the near-threshold states and can be examined by future lattice calculation.
Omer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 198, p.110241_1 - 110241_7, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Chemistry, Physical)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-014, 106 Pages, 2022/08
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of technology for rapid analysis of strontium-90 with low isotopic abundance using laser resonance ionization" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to develop a rapid analysis technique for strontium-90 using diode laser-based resonance ionization with elemental and isotopic selectivity. Strontium-90 is one of the major difficult-to-measure nuclides released into the environment due to the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Matsuda, Shohei; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Toru; Kaneta, Yui; Simonnet, M.; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Honda, Mitsunori; Shimojo, Kojiro; Doi, Reisuke; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 8(20), p.eabn1991_1 - eabn1991_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:58.16(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
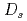 states
statesYang, Z.*; Wang, G.-J.*; Wu, J.-J.*; Oka, Makoto; Zhu, S.-L.*
Physical Review Letters, 128(11), p.112001_1 - 112001_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:96.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A novel framework is proposed to extract near-threshold resonant states from finite-volume energy levels of lattice QCD and is applied to elucidate structures of the positive parity 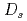 . The quark model, the quark-pair-creation mechanism and
. The quark model, the quark-pair-creation mechanism and 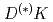 interaction are incorporated into the Hamiltonian effective field theory. The bare
interaction are incorporated into the Hamiltonian effective field theory. The bare 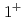
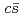 states are almost purely given by the states with heavy-quark spin bases. The physical
states are almost purely given by the states with heavy-quark spin bases. The physical 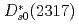 and
and 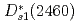 are the mixtures of bare
are the mixtures of bare 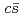 core and
core and 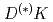 component, while the
component, while the 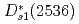 and
and 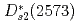 are almost dominated by bare
are almost dominated by bare 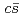 . Furthermore, our model well reproduce the clear level crossing of the
. Furthermore, our model well reproduce the clear level crossing of the 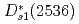 with the scattering state at a finite volume.
with the scattering state at a finite volume.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2021-050, 82 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "The study of oxidative stress status in the organs exposed to low dose/low dose-rate radiation" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to investigate the biological effects of low dose/low dose-rate radiation exposure, which is of great social interest, on the oxidative stress status of individual organs and will contribute to the collection of scientific data in a dose range to be required. An interdisciplinary collaborative study discussed the correlation between radiation dose and the biological effect by analyzing the samples of wild Japanese macaques exposed to radiation due to the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and of animal experiments.
Hashimoto, Shunsuke*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamada, Takeshi*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 342, p.117580_1 - 117580_8, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27(Chemistry, Physical)Quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) and pulsed-field-gradient nuclear magnetic resonance (PFGNMR) analyses of a nanofluid composed of silicon dioxide (SiO ) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO
) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO
particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO nanofluids.
nanofluids.
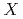 (3872)
(3872)Meng, L.*; Wang, G.-J.*; Wang, B.*; Zhu, S.-L.*
Physical Review D, 104(9), p.094003_1 - 094003_8, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:81.3(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The isospin violating decays of 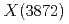 are revisited in a coupled-channel effective field theory. In a cutoff-independent formalism, we relate the coupling constants of
are revisited in a coupled-channel effective field theory. In a cutoff-independent formalism, we relate the coupling constants of 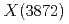 with the two channels to the molecular wave function. The isospin violating decays of
with the two channels to the molecular wave function. The isospin violating decays of 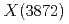 are obtained by two equivalent approaches, which amend some deficiencies about this issue in literature. In the quantum field theory approach, the isospin violating decays arise from the coupling constants of
are obtained by two equivalent approaches, which amend some deficiencies about this issue in literature. In the quantum field theory approach, the isospin violating decays arise from the coupling constants of 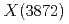 to two di-meson channels. In the quantum mechanics approach, the isospin violating is attributed to wave functions at the origin. We bridge the isospin violating decays of
to two di-meson channels. In the quantum mechanics approach, the isospin violating is attributed to wave functions at the origin. We bridge the isospin violating decays of 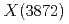 to its inner structure. Our results show that the proportion of the neutral channel in
to its inner structure. Our results show that the proportion of the neutral channel in 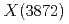 is over 80%. As a by-product, we find that the strong decay width and radiative decay width are about 30 keV and 10 keV, respectively, for the binding energy from -300 keV to -50 keV.
is over 80%. As a by-product, we find that the strong decay width and radiative decay width are about 30 keV and 10 keV, respectively, for the binding energy from -300 keV to -50 keV.
Harada, Hideo
Applied Sciences (Internet), 11(14), p.6558_1 - 6558_20, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)For accuracy improvement of neutron activation analysis and neutron capture cross section, bias effects are investigated on g- and s-factors in the Westcott convention. As origins of biases, a joining function shape, neutron temperature and sample temperature, have been investigated. Biases are quantitatively deduced for two 1/v isotopes ( Au,
Au,  Co) and six non-1/v isotopes (
Co) and six non-1/v isotopes ( Am,
Am,  Eu,
Eu, 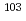 Rh,
Rh,  In,
In,  Hf,
Hf,  Ra). The s-factor calculated with a joining function deduced recently by a detailed Monte Carlo simulation is compared to s-factors calculated with traditional joining functions by Westcott. The results show the bias induced by sample temperature is small as the order of 0.1% for g-factor and the order of 1% for s-factor. On the other hand, biases induced by a joining function shape for s-factor depend significantly on both isotopes and neutron temperature. As the result, reaction rates are also affected significantly as well. The bias size on reaction rate is given in the case of epithermal neutron index r = 0.1, for the eight isotopes.
Ra). The s-factor calculated with a joining function deduced recently by a detailed Monte Carlo simulation is compared to s-factors calculated with traditional joining functions by Westcott. The results show the bias induced by sample temperature is small as the order of 0.1% for g-factor and the order of 1% for s-factor. On the other hand, biases induced by a joining function shape for s-factor depend significantly on both isotopes and neutron temperature. As the result, reaction rates are also affected significantly as well. The bias size on reaction rate is given in the case of epithermal neutron index r = 0.1, for the eight isotopes.
 Am(n,
Am(n, )
)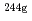 Am and
Am and  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)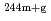 Am reactions
Am reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(3), p.259 - 277, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Research and development were made for accuracy improvement of neutron capture cross section data on  Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay
Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay  rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of
rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of  Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of
Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of  Am was examined by
Am was examined by  -ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by
-ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by  -ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the
-ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)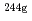 Am and for
Am and for  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)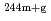 Am reactions.
Am reactions.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2020-048, 49 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "The study of oxidative stress status in the organs exposed to low dose/low dose-rate radiation". This study investigates the biological effects of low dose/low dose-rate radiation exposure, which is of great social interest, on the oxidative stress status of individual organs and will contribute to the collection of scientific data in a dose range to be required. An interdisciplinary collaborative study discussed the correlation between radiation dose and the biological effect by analyzing the samples of wild Japanese macaques exposed to radiation due to the accident of Fukushima nuclear power station and of animal experiments.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2020-024, 75 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Technology for Rapid Analysis of Strontium-90 with Low Isotopic Abundance using Laser Resonance Ionization" conducted in FY2019. In this study, we will develop a rapid analysis technique for strontium-90 using diode laser-based resonance ionization with elemental and isotopic selectivity. Strontium-90 is one of the major difficult-to-measure nuclides released into the environment due to the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Our method is particularly intended for real samples which contain high concentrations of strontium stable isotopes such as marine samples.
Baba, Yuji*; Shimoyama, Iwao
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 987, p.164845_1 - 164845_5, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.88(Instruments & Instrumentation)Multi-atom resonance (MAR) effect following the core-level resonant photoexcitation has been investigated for simple binary compounds such as CaCl , KCl and SrCl
, KCl and SrCl . For solid CaCl
. For solid CaCl , it was found that the intensity of Cl K
, it was found that the intensity of Cl K X-rays was reduced when the energy of the incident X-rays was tuned at the resonance energy of the neighboring Ca K-edge, but such intensity reduction was not observed for aqueous solution of CaCl
X-rays was reduced when the energy of the incident X-rays was tuned at the resonance energy of the neighboring Ca K-edge, but such intensity reduction was not observed for aqueous solution of CaCl . Similar results were also obtained for the KCl and SrCl
. Similar results were also obtained for the KCl and SrCl . From these results, it was clarified that for these binary compounds, the multi-atom resonance does occur only in an atom that is directly bound to the excited atom.
. From these results, it was clarified that for these binary compounds, the multi-atom resonance does occur only in an atom that is directly bound to the excited atom.
Harada, Hideo; Takayama, Naoki; Komeda, Masao
Journal of Physics Communications (Internet), 4(8), p.085004_1 - 085004_17, 2020/08
A new convention of epithermal neutron spectrum is formulated for improving accuracy of resonance integrals. The new type function is proposed as an approximating function of epithermal neutron spectrum based on calculations by the state-of-art Monte Carlo code MVP-3. Bias effects on determination of resonance integrals due to utilizing approximating functions of the traditional types and the new type are compared. The other bias effect is also investigated, which is caused by neglecting position dependence of a neutron spectrum inside an irradiation capsule. For demonstrating the bias effects due to these assumptions on neutron spectrum quantitatively in a practical case, the thermal neutron-capture cross section and resonance integral of  Cs measured at a research reactor JRR-3 are re-evaluated. A superior property of the proposed new convention is discussed. The experimental method is proposed to determine the new shape factor
Cs measured at a research reactor JRR-3 are re-evaluated. A superior property of the proposed new convention is discussed. The experimental method is proposed to determine the new shape factor  introduced in the convention by a combinational use of triple flux monitors (
introduced in the convention by a combinational use of triple flux monitors ( Au,
Au,  Co and
Co and  Zr), and its analytical methodology is formulated.
Zr), and its analytical methodology is formulated.